Chronic prostatitis is an inflammatory disease of the prostate gland, which is characterized by organic tissue changes and functional disorders of the prostate, male reproductive system and urinary tract.
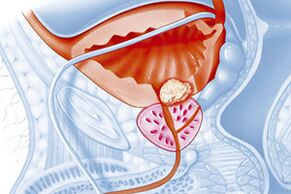
The prostate is a tubular alveolar gland found only in men. This gland is involved in the production of sperm and is located below the bladder around the beginning of the urethra. Chronic prostatitis in men can occur due to infection in the prostate gland from the bladder through the blood and lymphatic vessels of the pelvis or in another way. Although the presence of an infection may not cause illness or impotence, it usually does not go away for a man without a trace. At the moment, the man is observing a decrease in the hardness of the penis, sexual dysfunctions during sex and urinary disorders.
Chronic prostatitis does not threaten a man's life, but it can still cause psychological distress and deterioration in family relationships. It should also be noted that, according to experts, chronic prostatitis, namely its untimely treatment, can lead not only to the development of serious complications, but also to prostate cancer. Indeed, in addition to infection, there are a number of other factors predisposing to chronic prostatitis. Nevertheless, the manifestation and exacerbation of chronic prostatitis has different specifics.
Stages of chronic prostatitis
Although there is still no single specificity for the development of chronic prostatitis, experts distinguish the following types of it:
- I acute bacterial prostatitis;
- II prostatitis of bacterial genesis. It is most commonly found;
- III chronic non-bacterial prostatitis is a symptom complex of chronic pelvic pain, the duration of which is more than 3 months;
- category III A is a type of inflammatory form of chronic prostatitis with an increased level of leukocytes in the secretion of the prostate;
- III B is a non-inflammatory form of chronic prostatitis without an increased level of leukocytes and pathogens in the secretion of the prostate;
- Type IV is diagnosed as asymptomatic chronic prostatitis, which does not cause pain and is detected completely by chance based on the results of the analysis of prostate secretion or its biopsy.
The frequency and causes of this category of chronic prostatitis are still not known. As for the reasons for the development of other types of the disease, it should be noted here that they can be caused by the penetration of various infectious microorganisms into the ureter, as well as by a violation of various functions in the man's body.
Preventive methods of prostate inflammation
Chronic prostatitis requires long-term treatment. Therefore, it is better to follow preventive measures to avoid it. To do this, the patient will only need to make some adjustments to his lifestyle, which will not only be beneficial for the general state of health, but also relieve this disease. So, first of all, the following prevention rules must be observed:
- strive to lead a healthy lifestyle;
- completely exclude spicy foods from the diet;
- do not abuse alcohol;
- playing sports, including exercise that helps strengthen muscles and improve blood circulation in the pelvic organs;
- attend yoga classes at will;
- observe methods of prevention and treatment of infectious diseases;
- eliminate pelvic congestion and promptly treat rectal diseases;
- exclude excessive masturbation;
- try to have a regular, but at the same time safe sex life;
- avoid hypothermia;
- do not sit on cold surfaces;
- during sedentary work, warm up more often.
In addition to these preventive measures, men should take into account the fact that chronic prostatitis manifests itself insignificantly. Therefore, if a man observes discharge during urination or defecation, and also experiences mild pain, then in this case it is worthwhile to immediately consult a doctor. It is also worth remembering that the course of treatment should be carried out strictly under the supervision of a specialist without any neglect. In addition, the selection of drugs during antibiotic therapy is carried out according to the individual condition of the patient and only after he undergoes special studies. The intake of prescribed medications should not be interrupted, and even more so, additional medications should not be taken without a doctor's prescription. Don't delay your doctor's appointment. By searching on our website, you can easily find a clinic that is suitable for both location and price policy.
Causes of prostate inflammation
Chronic prostatitis in medicine is positioned as a polyetiological disease. In addition to the penetration of infection into the ureteral organs, it can occur and recur due to the appearance of neurovegetative and hemodynamic disorders, as well as a weakening of the immune system and autoimmune, hormonal or biochemical processes. Inflammation of the prostate gland can develop against the background of diseases such as:
- depression;
- neurogenic bladder dysfunction;
- reflex sympathetic dystrophy;
- inflammatory processes of nearby organs located;
- bladder neck hypertrophy;
- prostate adenoma;
- stricture of the urethra;
- diseases of the rectum.
Given these factors, the following reasons are attributed to the risk of developing prostate inflammation:
- a sedentary lifestyle, especially in a sitting position, entails a dysfunction of the blood supply to the pelvic organs;
- local hypothermia of the body;
- frequent constipation;
- irregular sexual relations or sudden exertion;
- chronic infections;
- previous sexually transmitted diseases. In particular, their untimely treatment;
- improper nutrition;
- lack of sleep;
- chronic stress.
In addition, chronic non-bacterial prostatitis can be caused by the formation of myofascial trigger points during the course of diseases, injuries and surgical interventions on the pelvic organs.
Chronic prostatitis symptoms

Symptoms of chronic prostatitis do not bother the man much. Inflammation of the prostate occurs suddenly. The patient may be disturbed by acute pain in the perineum and groin area, and may also experience pain during urination and defecation, accompanied by discharge from the urethra. All of these signs of chronic prostatitis can be accompanied by fever, fever, and fever. Most often, these symptoms are intermittent. Also, chronic prostatitis can be expressed in the form of complications of sexually transmitted diseases. During the course of the disease, the patient may feel discomfort when urinating, pain in the perineum, as well as the manifestation of discharge. Chronic inflammation of the prostate leads to erectile dysfunction and slowing down of ejaculation.
The inflammatory process of the prostate moves deep into the urinary system, which can lead to cystitis and pyelonephritis. Most often, these exacerbations end with inflammation of the testicles and appendages, which entails infertility, requiring long-term treatment. Therefore, you should not postpone going to the doctor. Timely diagnosis and treatment is required. It is important to remember that chronic prostatitis can be cured if the disease is not triggered.
Diagnostics of the chronic prostatitis
As a rule, a doctor can diagnose one or another type of chronic prostatitis based on the complaints indicated by the patient or after an examination. First, the specialist palpates the prostate gland, and then recommends that the patient do a laboratory study of the urine culture tank and prostate secretion. This diagnosis allows you to determine the further treatment of chronic prostatitis. In addition, a urologist can apply diagnostic methods such as:
- transrectal ultrasound, which allows you to determine the size and volume of the prostate, as well as to identify the presence of neoplasms;
- determination of the urethral pressure profile makes it possible to find out the cause of urinary disorders and the functions of the pelvic floor muscles;
- microscopic examination of scraping of the mucous membrane of the urethra, which helps to determine the presence of a specific flora that causes infectious diseases; X-ray of the prostate;
- MRI of the pelvic organs, which helps differentiate with prostate cancer, as well as identify a non-inflammatory type of bacterial prostatitis;
- determination of the state of humoral and cellular immunity in the secretion of the prostate. This kind of research helps not only to diagnose the category of the inflammatory process of the prostate gland, but also to solve the question of which method can be used to cure chronic prostatitis.
Chronic prostatitis treatment
Chronic prostatitis is considered an insidious and complex disease, the method of its treatment requires an integrated approach. Urologists use treatments such as:
- antibiotic therapy, during which medications are prescribed that destroy the hidden microorganisms of the infection. The patient takes these drugs for several weeks. In the absence of the proper effect, antibiotics can be replaced with another group of drugs;
- physiotherapy can include exposure to electromagnetic, ultrasonic and laser waves, which significantly increases the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy;
- magnetic laser therapy has an anti-congestive effect and improves blood microcirculation in the pelvic organs;
- transrectal prostate massage is the most painful and uncomfortable method of treatment, but at the same time the most effective. It is based on the elimination of the inflammatory secretion by squeezing it out with a finger;
- darsonvalization;
- electrophoresis with drugs;
- hormone therapy;
- transurethral electrosurgery. This method of treatment can be used only in the case of complications that, in addition to disorders of the urination process or reproductive function in a man, have led to the onset of sclerosis of the prostate and bladder neck. If, after surgery, an exacerbation of the chronic inflammatory process is observed, then in this case, the patient can remove the entire remaining gland;
- immunocorrection is aimed not only at eliminating the infection, but also at completely eliminating its reappearance. This method of treatment implies the normalization of the lifestyle, which entails an active lifestyle, regular walks, adherence to the daily regimen and proper nutrition;
- Spa treatment.
In addition, the prescribed treatment for chronic prostatitis may include a visit to an immunologist and additional special tests. Since the termination of this or that course of therapy does not guarantee the complete destruction of the prostatitis infection, therefore, there is a possibility that it will reoccur. To cure chronic prostatitis, the patient should strictly follow all the doctor's recommendations and complete the prescribed course of treatment to the end.